About DIET Chennai
Roots and evolution of DIET, Chennai
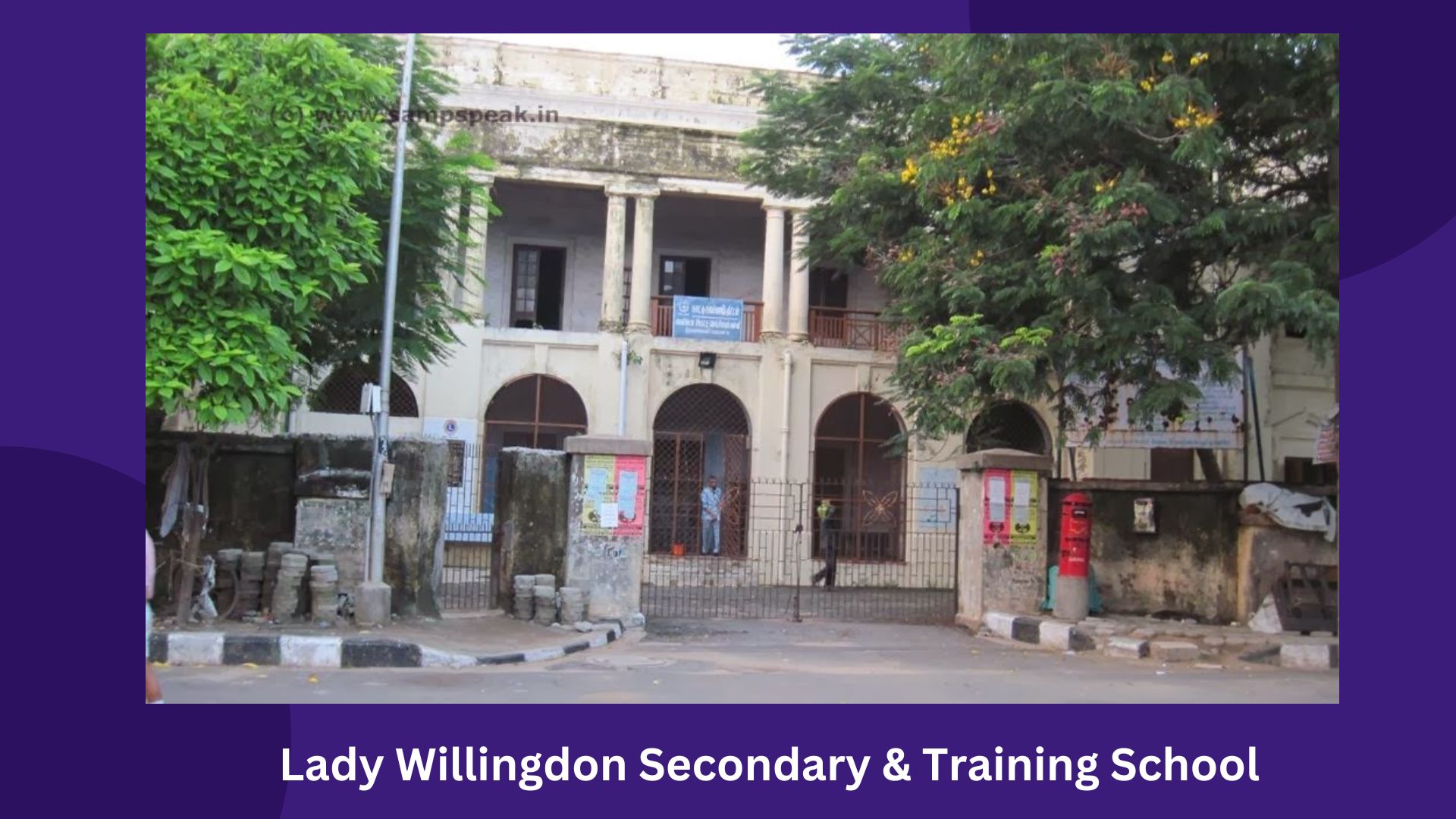
DIET, Chennai is a premier Teacher Education Institution (TEI) situated in the Lady Willingdon Educational Campus, Kamarajar Salai (opposite to Marina Beach), Triplicane, Chennai, Tamil Nadu. It functions under the State Council of Educational Research and Training (SCERT), Tamil Nadu.
1. Origins (1912)
The roots of the Lady Willingdon Training School trace back to 1912, with the establishment of a school and hostel for young widow children in T.P. Koil Street, Triplicane, Chennai. This pioneering initiative emerged from the social reform movement focused on improving the lives of child widows and marginalized girls in early 20th-century Madras.
Padmashri R.S. Subbalakshmi, a leading social reformer and educator, was instrumental in conceptualizing and founding the institution (Felton, 1950). She was supported by Mrs. C. Drysdale, then Director of Education for Girls and Women, and Miss Prager, Assistant Inspectress, Southern Circle, who both represented official commitment from the colonial educational administration (Felton, 1950).
2. Relocation to the Ice House (1914)
By 1914, the institution had moved to the Ice House, now known as Vivekanandar Illam, located on Marina Beach. This move was made initially on a rental basis, offering a more expansive location for the growing institution. Mrs. C. Drysdale, then Additional Director of Education for Girls and Women convinced the Department of Public Instruction and the Madras Presidency to purchase the Ice House to run the Widows hostel and the attached school. At this stage, the school was called the Widows Teacher Training Institute.
3. Renaming as Lady Willingdon Training School (1922)
On December 19, 1922, a new purpose-built block was completed, and the institution was officially named Lady Willingdon Training School, in honor of Lady Willingdon, the wife of the then-Governor of Madras (The Hindu, 2024).
During this period, the Government of Madras expanded the campus by acquiring nearby land from M. Singaravelar, a prominent landholder and labor rights activist, through the Madras Land Reforms Act (THE HIGH COURT OF JUDICATURE AT MADRAS, WP 19839 & 19840 of 2013 dated 17.11.2015). This land enabled further construction and separation of academic wings.
4. Courses in Elementary Teacher Training
Over the decades, the institute offered several programs aimed at producing skilled elementary teachers, such as:
- * Junior Grade Basic Training Certificate
- * Senior Grade Basic Training Certificate
- * Diploma in Teacher Education (D.T.Ed.,)
- * Diploma in Elementary Education (D.El.Ed.,)
These courses emphasized pedagogy, child psychology, school practice, and classroom methods aligned with state curriculum frameworks.
5. Upgradation to DIET and IASE – 1990
Following the recommendations of the National Policy on Education, 1986, and the resulting teacher education reforms, the institutions were further upgraded in 1990:
- 🏫 The Lady Willingdon Teacher Training Institute became the District Institute of Education and Training (DIET), Chennai
- 🏫 The Lady Willingdon Teacher Training College became the Institute of Advanced Study in Education (IASE), Chennai
These changes positioned the institutions to support curriculum innovation, in-service teacher training, and research-driven education planning at both state and national levels (National Policy on Education, 1986).
6. Institutional Split and Establishment of Training College
In the 1990s, the training institution was bifurcated into two separate entities:
- ✍️ The Lady Willingdon Teacher Training Institute, focused on elementary education
- ✍️ The Lady Willingdon Teacher Training College, offering advanced teacher education programs
This administrative and academic split allowed both institutions to specialize in their respective domains and meet evolving educational standards.
7. Legacy and Contemporary Role
Today, more than a century since its founding, the legacy of the Lady Willingdon institutions remains significant in Tamil Nadu's teacher education landscape:
- 🎯DIET Chennai continues to train elementary teachers and provide support for Continuous Professional Development of Teachers from Pre-primary to Class 12 and develop district-level academic support systems.
- 🎯Lady Willingdon IASE Chennai is recognized as a hub for education and research in teacher education.
Together, they reflect the pioneering spirit of Padmashri R.S. Subbalakshmi and her associates, who envisioned education as a tool for empowerment, especially for women and marginalized communities.



References
- Felton, M. (1950). A child widow’s story: The autobiography of R.S. Subbalakshmi. London: Victor Gollancz Ltd.
- Forbes, G. (1996). Women in Modern India (1st ed.). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CHOL9780521268127
- Mangal, A. (2020). A century of teacher education in India: 1883-1985. Espacio, Tiempo y Educación, 7(1), 263–285.
- Kundu, C. (2017). TRAINING OF VERNACULAR TEACHERS IN PRE-INDEPENDENT INDIA IN THE FIRST HALF OF TWENTIETH CENTURY. International Education and Research Journal (IERJ), 3(6). https://ierj.in/journal/index.php/ierj/article/view/1141
- NCERT. (1970). ELEMENTARY TEACHER EDUCATION. NCERT.
- Government of India. (1986). National Policy on Education. Ministry of Human Resource Development.
- The Hindu. (2023, September 16).A centurion still around. Retrieved from The Hindu Archive
- Lady Willingdon Institute of Advanced Study in Education. (n.d.). Official website. Retrieved from https://lwiase.ac.in
- Madras Musings. (n.d.). Archive on Madras land and educational institutions. Retrieved from http://archive.madrasmusings.com
- The Hindu. (2024, Sept. 1). A school caters to women’s empowerment. Retrieved from The Hindu Archive